Does Ibuprofen Raise Blood Pressure?
Yes, ibuprofen can increase blood pressure significantly. As a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), ibuprofen inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. This blocks the production of prostaglandins, the lipid compounds that keep the kidney’s blood vessels dilated. When those vessels constrict, the kidneys hold on to sodium and water, which increases total blood volume and systemic vascular resistance.
Table of Contents
Research shows that regular use can raise mean arterial pressure by 3 to 6 mmHg. That may sound small, but it is enough to cancel out the benefits of many blood pressure medications, especially ACE inhibitors and diuretics, and it can drastically raise the risk of cardiovascular events in vulnerable patients.
The Hidden Danger in Your Medicine Cabinet
You wake up with a stiff neck or a pounding headache. Without thinking, you reach into the medicine cabinet for a bottle of relief. It is an automatic reflex for millions of people. But for the nearly 50% of American adults who are managing hypertension, this simple act comes with a risk most people never consider. The question, “Can ibuprofen increase blood pressure?” is one of the most important things a patient can ask. Yet, the answer is usually buried in fine print or brushed off as a minor side effect.
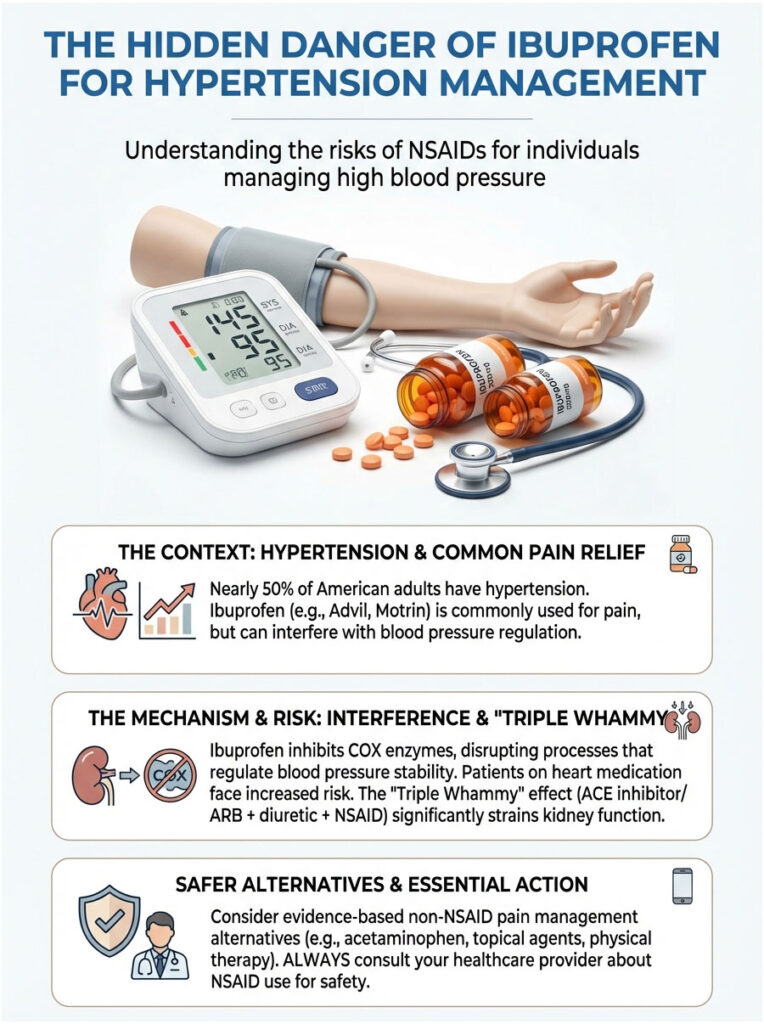
Ibuprofen, sold under familiar names like Advil and Motrin, is a household staple worldwide. It works well, it is cheap, and it is generally safe for healthy people. But its mechanism of action puts it in direct conflict with your body’s ability to maintain stable blood pressure. As a specialist in cardiovascular pharmacology, I regularly see patients whose blood pressure is perfectly controlled on medication, only to watch their numbers spike without explanation. When we review their history, the culprit is almost always the same: daily use of an over-the-counter NSAID for a nagging injury.
This article goes well beyond basic advice. We will break down the physiological mechanics of how ibuprofen increases blood pressure through COX enzyme inhibition. We will look at the specific dangers for people on heart medication, analyze the “Triple Whammy” effect on the kidneys, and cover evidence-based alternatives that let you manage pain without putting your cardiovascular health at risk.
Key Statistics: NSAIDs and Hypertension
- 3 to 6 mmHg: The average increase in mean arterial pressure caused by regular NSAID use.
- 19%: The increased risk of hospital admission for heart failure among current NSAID users.
- 45%: The percentage of American adults living with hypertension, making this interaction a widespread public health concern.
- 2015: The year the FDA strengthened warnings about non-aspirin NSAIDs and the risk of heart attack or stroke.
- 88%: The percentage of elderly patients who use NSAIDs regularly, despite being the highest-risk group.
The Physiology: How NSAIDs Disrupt Your Blood Pressure
To truly understand why the answer to “can ibuprofen increase blood pressure” is a definitive yes, we need to look beyond the heart and focus on the kidneys. The kidneys are not just waste filters. They are the master regulators of blood pressure in the human body. They control blood volume through sodium excretion and adjust vascular tone through hormone release. Ibuprofen disrupts this delicate balance at a cellular level.
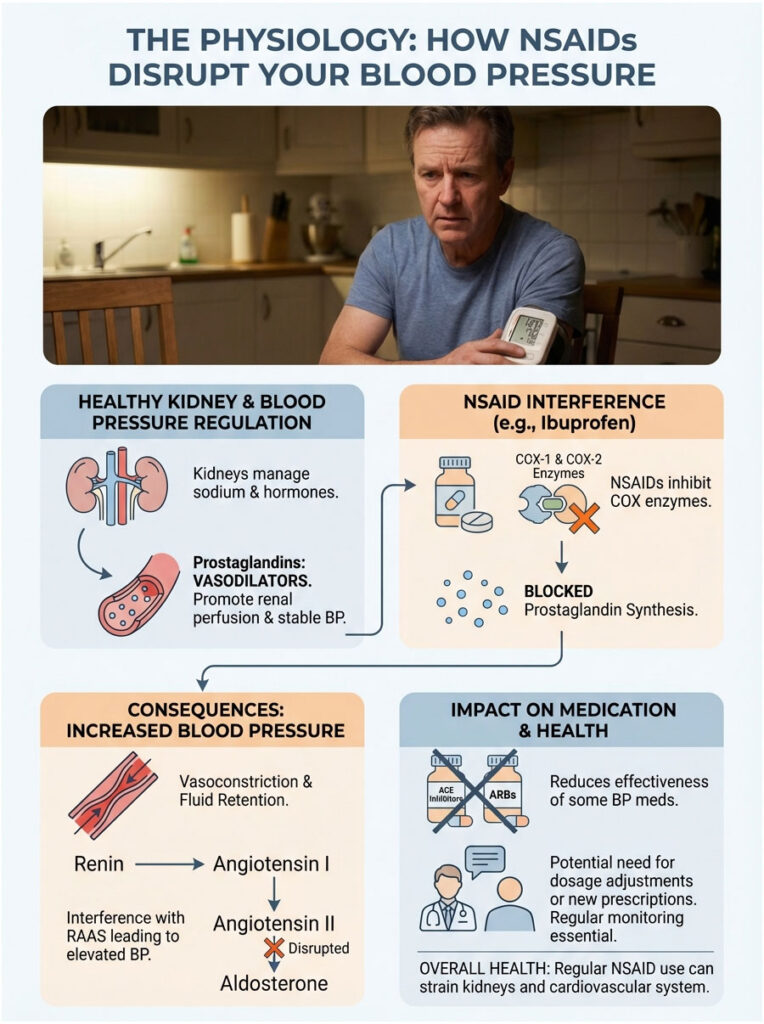
The Role of Prostaglandins: Your Kidney’s Safety Valve
Most people only associate prostaglandins with pain and inflammation. And while they do carry pain signals, inside the renal system they serve a completely different, protective role. Prostaglandins are potent vasodilators. Under normal conditions, they keep the afferent arterioles, the small blood vessels that feed the kidney’s filtration units, wide open. This ensures that even when your body is stressed, dehydrated, or dealing with low blood pressure, your kidneys still receive adequate blood flow (renal perfusion).
Mechanism of Action: COX Inhibition
Ibuprofen belongs to the NSAID class of drugs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs). It works by inhibiting enzymes called Cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). These enzymes convert arachidonic acid into prostaglandins. By blocking them, ibuprofen effectively shuts down prostaglandin production. While this successfully stops the pain signal in your knee or back, it simultaneously removes the “safety valve” in your kidneys.
The Hemodynamic Domino Effect
Once prostaglandin synthesis is blocked, a chain reaction kicks in that drives blood pressure upward:
- Renal Vasoconstriction: Without the dilating effect of prostaglandins, the afferent arterioles in the kidney constrict. This increases resistance to blood flow within the kidneys, a state known as increased renal vascular resistance.
- Sodium and Water Retention: When the kidneys sense reduced blood flow, they interpret it as dehydration or low blood volume. In response, they aggressively reabsorb sodium. Where sodium goes, water follows. This leads to fluid retention and an expansion of total blood volume.
- Increased Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR): Narrowed blood vessels combined with increased fluid volume forces the heart to pump against higher resistance. This mechanical stress registers as elevated blood pressure on your cuff.
Interference with the RAAS System
The disruption does not stop there. NSAIDs can suppress the initial release of renin, but the resulting sodium retention throws off the feedback loops of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS). For patients taking ACE inhibitors (like Lisinopril) or ARBs (like Losartan), this is a real problem. These drugs are trying to relax your blood vessels, while ibuprofen is chemically fighting to constrict them. This tug-of-war makes blood pressure medication significantly less effective and often forces dosage adjustments or additional prescriptions just to maintain control.
What the Clinical Data Actually Shows
In clinical practice, we deal with hard numbers. Patients often want to know whether the risk is theoretical or real. The data confirms that it is measurable, significant, and reproducible.

The “3 to 6 mmHg” Metric
Meta-analyses and clinical trials have consistently linked NSAID use with an elevation in mean arterial pressure of roughly 3 to 6 mmHg. To someone without a medical background, that number sounds trivial. But in epidemiology and cardiology, it is a massive shift. Research shows that a permanent increase of just 5 mmHg in diastolic blood pressure is associated with a 34% increase in stroke risk and a 21% increase in coronary heart disease risk. For a patient already hovering near the borderline of hypertension, ibuprofen can be the single factor that pushes them into a danger zone.
The FDA Boxed Warning (2015)
The Food and Drug Administration takes this seriously. In 2015, the FDA strengthened existing label warnings for non-aspirin NSAIDs. The updated warning states that the risk of heart attack and stroke can begin within the first weeks of NSAID use. The risk appears to be greater at higher doses. The agency explicitly noted that there is no period of use shown to be risk-free. This regulatory stance reinforces the medical consensus: yes, ibuprofen can increase blood pressure, and it can do so quickly enough to trigger cardiovascular events.
The PRECISION Trial Findings
The PRECISION trial was a landmark study that evaluated the comparative cardiovascular safety of ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib. While the study was complex, one of the key takeaways for hypertensive patients was clear. Ibuprofen was associated with a higher incidence of significantly elevated blood pressure compared to celecoxib. The trial highlighted that not all NSAIDs affect the kidneys equally, but ibuprofen remains a major offender when it comes to hemodynamic instability. It underscored the need for individualized risk assessment when prescribing pain relief to cardiac patients.
The “Triple Whammy”: A Drug Interaction You Need to Know About
If you take medication for high blood pressure, you need to understand the “Triple Whammy.” This is a term used in pharmacy and nephrology to describe a specific, dangerous drug combination that can lead to acute kidney failure.
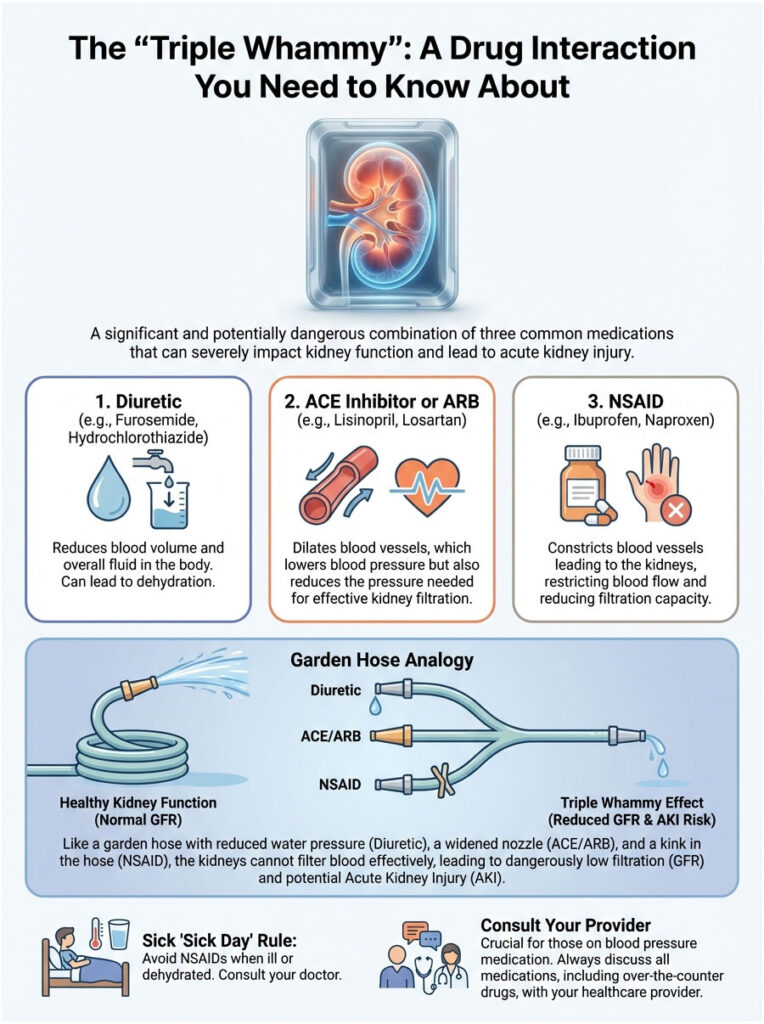
The Three Drugs Involved
The Triple Whammy occurs when a patient takes all three of these at the same time:
- A Diuretic: Often called a “water pill” (e.g., Hydrochlorothiazide or Furosemide).
- A RAAS Inhibitor: An ACE Inhibitor (e.g., Lisinopril) or an Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (e.g., Losartan).
- An NSAID: Such as ibuprofen or naproxen.
How It Leads to Kidney Failure
Each of these drugs affects the kidney’s filtration rate (GFR) in a different way. The diuretic reduces blood volume, which lowers the pressure entering the kidney. The ACE inhibitor or ARB dilates the efferent arteriole (the exit vessel), reducing filtration pressure inside the kidney. The NSAID constricts the afferent arteriole (the entrance vessel).
Think of it like a garden hose. You turn down the faucet (NSAID), you poke holes in the hose to let water leak out (diuretic), and you remove the nozzle at the end that creates back-pressure (ACE inhibitor). Water stops flowing. In the body, this means the kidneys stop filtering toxins. The result can be Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), which may require hospitalization and potentially dialysis. If you are already on the first two drugs, the answer to “can ibuprofen increase blood pressure and damage my kidneys” is a clear yes.
The “Sick Day” Rule
If you are taking blood pressure medication and come down with a fever or illness that causes dehydration (vomiting, diarrhea), avoid NSAIDs completely. Your kidneys are already under stress from fluid loss. Adding ibuprofen at that moment dramatically spikes the risk of acute kidney injury.
Ibuprofen vs. Other Pain Relievers: A Comparison
Patients often ask if switching to a different pain reliever makes a difference. Is Aleve safer than Advil? What about Tylenol? Understanding the risk hierarchy is essential for safe pain management.
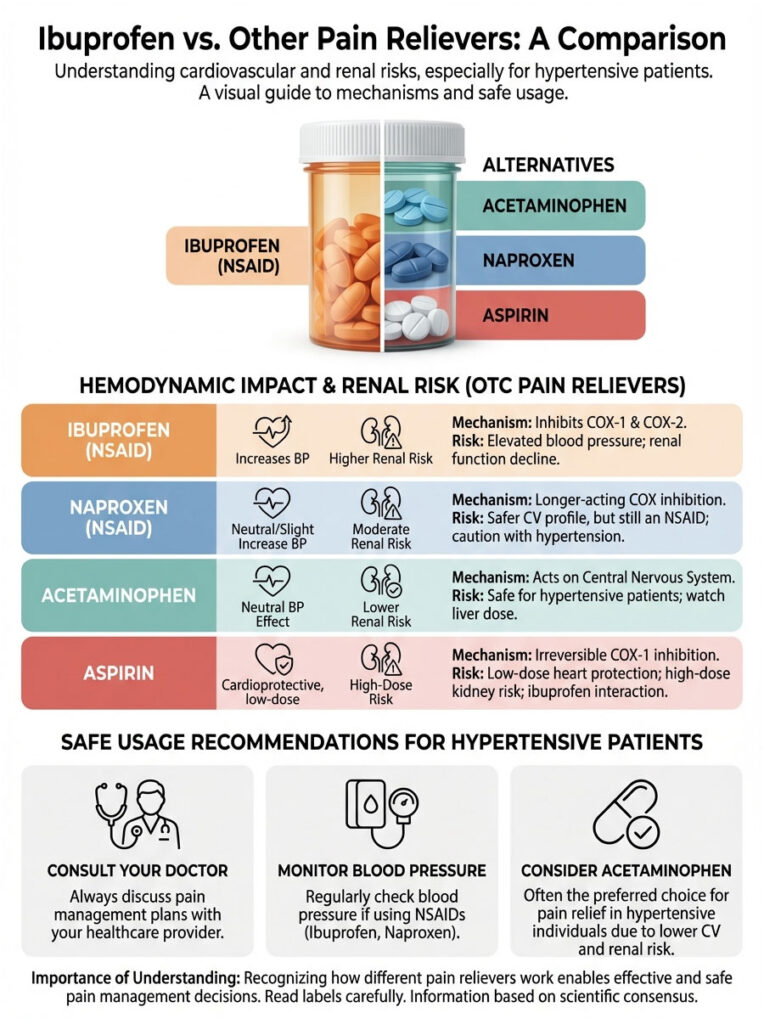
Naproxen (Aleve)
Naproxen is sometimes cited in older studies as having a “safer” cardiovascular profile compared to ibuprofen, particularly regarding heart attack risk. However, when it comes to blood pressure specifically, naproxen is still an NSAID. It still inhibits COX enzymes and still causes sodium retention. While it may be slightly less thrombotic (less likely to cause clots), it can still destabilize blood pressure control in hypertensive patients.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
Acetaminophen operates through a completely different mechanism. It works primarily on the central nervous system rather than peripheral tissues. It does not inhibit prostaglandins in the kidneys to any meaningful degree, so it does not cause vasoconstriction or sodium retention. For this reason, it is the first-line recommendation for pain relief in patients with hypertension.
Aspirin
Aspirin is technically an NSAID, but it stands apart. Low-dose aspirin (81mg) is used for its anti-platelet (blood-thinning) properties to prevent heart attacks. However, high-dose aspirin taken for pain can still affect the kidneys. There is also a critical interaction to be aware of: ibuprofen can block the anti-platelet effect of aspirin if the two are taken too close together. If you take daily aspirin for heart protection, ibuprofen may render that protection useless.
Comparison Table: Hemodynamic Impact of Common OTC Pain Relievers
| Drug Class | Active Ingredient | Brand Examples | Impact on Blood Pressure | Renal Risk Level | Safe for Hypertensive Patients? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSAID | Ibuprofen | Advil, Motrin | Moderate to High Increase | High (Vasoconstriction) | No (Avoid if possible) |
| NSAID | Naproxen | Aleve | Moderate Increase | High | Caution (Consult Doctor) |
| Analgesic | Acetaminophen | Tylenol | Neutral / Minimal | Low | Yes (First Line) |
| Salicylate | Aspirin (Low Dose) | Bayer | Neutral | Low | Yes (For heart protection) |
| NSAID | Diclofenac (Topical) | Voltaren Gel | Low Risk | Low (Low absorption) | Yes (Preferred over oral NSAIDs) |
Who Is at Highest Risk?
While “can ibuprofen increase blood pressure” is a valid question for everyone, certain groups face far greater danger. In these populations, the body’s ability to handle fluid retention or vasoconstriction is already compromised.
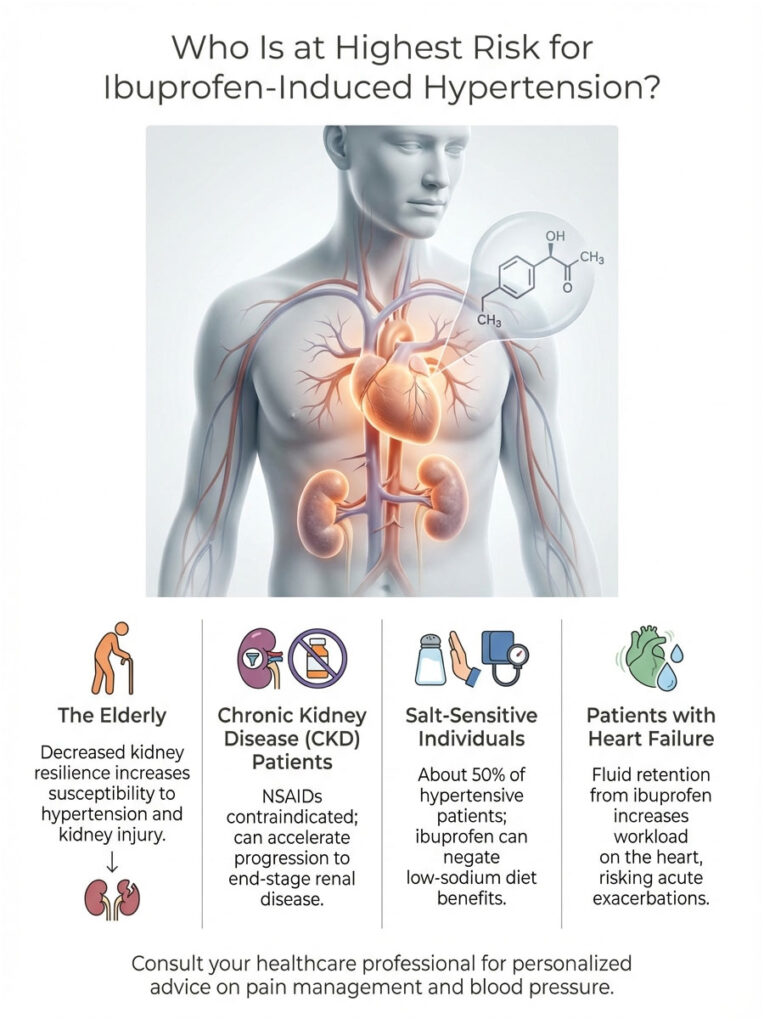
The Elderly
As we age, our Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR), the speed at which kidneys filter blood, naturally declines. An 80-year-old simply does not have the same kidney resilience as a 30-year-old. This makes elderly patients far more susceptible to NSAID-induced hypertension and kidney injury. In geriatric medicine, the goal is often to “deprescribe” NSAIDs entirely to preserve whatever renal function remains.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Patients
For patients with CKD (Stages 3-5), NSAIDs are generally contraindicated. Their kidneys are already struggling to filter waste and balance fluids. Introducing ibuprofen is like stepping on the brakes of a car that is already losing momentum. It can speed up the progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
Salt-Sensitive Individuals
About 50% of people with hypertension are “salt-sensitive,” meaning their blood pressure rises sharply in response to sodium intake. Because ibuprofen forces the kidneys to retain sodium, it mimics the effect of a high-salt diet. For these individuals, taking ibuprofen cancels out the benefits of eating low-sodium and drives pressure up aggressively.
Patients with Heart Failure
Heart failure patients depend on a delicate balance of fluid volume. Their hearts are too weak to pump excess fluid efficiently. Ibuprofen causes fluid retention (edema), which increases the workload on the failing heart. This can trigger an acute exacerbation of heart failure, leading to shortness of breath and hospitalization.
Safer Alternatives for Pain Management
Knowing that ibuprofen can increase blood pressure does not mean you have to live in pain. There are effective strategies for managing inflammation and discomfort that spare your kidneys and cardiovascular system.

Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
This should be your first choice for headaches or mild pain. While it lacks the anti-inflammatory strength of ibuprofen, it is hemodynamically neutral. Just make sure you do not exceed 3,000mg to 4,000mg per day to protect your liver.
Topical NSAIDs (Diclofenac / Voltaren Gel)
This is a genuine game-changer for patients with arthritis in the knees or hands. Topical NSAIDs like Voltaren Gel are applied directly to the skin over the painful joint. Systemic absorption is very low, roughly 6% compared to oral pills. That means you get high concentrations of the drug at the pain site, but very little reaches the kidneys. It is essentially a loophole that allows many hypertensive patients to use NSAIDs more safely.
Non-Drug Strategies
Physical therapy and biomechanics correction often address the root cause of pain rather than just masking it. Anti-inflammatory diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids (like the Mediterranean diet) can lower systemic inflammation over time. Turmeric and curcumin supplements have also shown promise in reducing inflammation. However, patients on blood thinners (like Warfarin or Eliquis) should consult their cardiologist before starting these, as they can increase bleeding risk.
Comparison Table: Safety Profile of Pain Management Options
| Strategy | Efficacy for Inflammation | Systemic Absorption | Risk of BP Spike | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Ibuprofen | High | 100% | High | Acute injury in healthy adults |
| Topical Diclofenac | Moderate/High (Local) | ~6% | Very Low | Arthritis in knees/hands for heart patients |
| Acetaminophen | Low (Anti-inflammatory) | High | None | Headaches, fever, non-inflammatory pain |
| Ice/Heat Therapy | Moderate | 0% | None | Acute muscle strain or chronic stiffness |
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you must take NSAIDs for a short period, staying vigilant is critical. Self-monitoring is the most effective tool you have.

Monitoring at Home
Do not rely on how you feel. High blood pressure is often completely silent. If you start a course of ibuprofen, check your blood pressure daily at home. If you notice a consistent upward trend, for example your systolic (top number) moving from 125 to 135 over three days, that is a clear sign the medication is affecting your hemodynamics.
Red Flags That Require Immediate Attention
Stop the medication and seek medical help if you experience:
- Sudden Weight Gain: Gaining 3 or more pounds in a week is physically impossible from food alone. This points to fluid retention.
- Edema: Noticeable swelling in the ankles, feet, or hands.
- Shortness of Breath: This may indicate fluid accumulating in the lungs.
- Systolic Pressure Above 140 mmHg: Or any reading significantly higher than the baseline target set by your doctor.
Chronic Use vs. Occasional Use: What Actually Matters
One of the most common questions patients ask involves duration. Is one pill dangerous? Does a week of treatment cause permanent damage? The relationship between NSAIDs and blood pressure is generally both dose-dependent and duration-dependent.
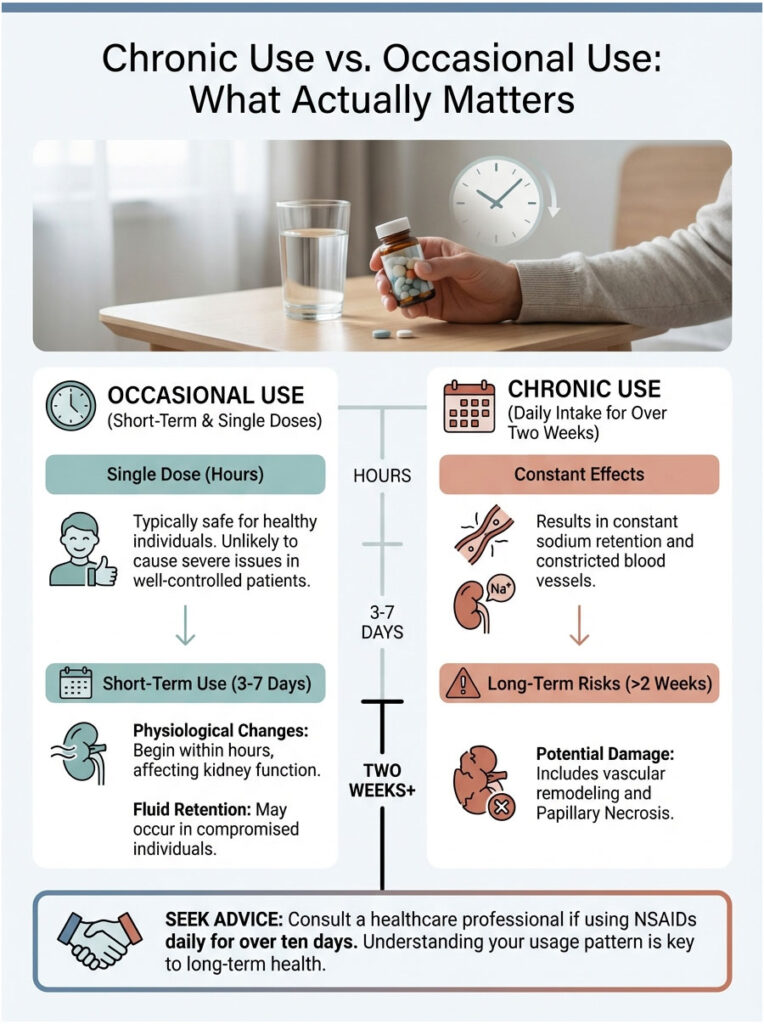
Short-Term Use
Taking a single dose of 400mg ibuprofen for a headache is unlikely to cause a hypertensive crisis in a well-controlled patient. However, the physiological changes start almost immediately. Within hours of ingestion, prostaglandin inhibition begins. For a healthy person, the kidneys compensate. For a person with compromised renal function, even short-term use (3-7 days) can produce noticeable fluid retention and blood pressure elevation.
Long-Term Use
The real danger lies in chronic use, defined as daily intake for more than two weeks. In chronic users, the body stays in a constant state of sodium retention. The blood vessels remain perpetually constricted. Over time, this leads to vascular remodeling, where the arteries become stiffer. Chronic NSAID use can also cause a condition called Papillary Necrosis, a form of permanent kidney damage. If you find yourself reaching for ibuprofen daily for more than ten days, see a doctor. It is better to investigate the root cause of your pain than to mask it with a medication that may be quietly harming you.
Lifestyle Factors That Make Things Worse
Drug interactions are not the only concern. Everyday lifestyle habits can compound the blood pressure effects of ibuprofen.

Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol acts as a mild diuretic and an initial vasodilator, followed by rebound vasoconstriction. Combining it with ibuprofen significantly raises the risk of gastric bleeding. From a blood pressure standpoint, heavy alcohol use raises BP on its own. Adding ibuprofen layers renal stress on top of existing liver stress.
High Sodium Diet
Ibuprofen causes sodium retention. If you eat a high-sodium diet (processed foods, fast food) while taking ibuprofen, you are fueling the fire. You are handing your kidneys massive amounts of salt to hoard. This combination virtually guarantees significant fluid retention and blood pressure spikes. Patients on NSAIDs should aim to keep sodium intake under 2,000mg per day to help offset the drug’s effects.
Dehydration
Dehydration is the kidney’s worst enemy. When you are dehydrated, your kidneys are already working overtime to conserve water. Introducing an NSAID, which constricts blood flow to the kidney, during a state of dehydration is a recipe for Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN). Always make sure you are well-hydrated if you absolutely must take an NSAID.
Final Takeaway
The question “can ibuprofen increase blood pressure” is not just academic. It is a practical safety concern for millions of people. Here is the clinical reality, distilled:
- Mechanism: Ibuprofen inhibits renal prostaglandins, leading to vasoconstriction and sodium retention, which directly raises blood pressure.
- Magnitude: The average increase is 3 to 6 mmHg, enough to raise stroke risk and counteract blood pressure medications.
- Triple Whammy: Combining ibuprofen with diuretics and ACE inhibitors or ARBs creates a high risk for acute kidney failure.
- Best Practice: Hypertensive patients should prioritize acetaminophen or topical NSAIDs (diclofenac) and avoid oral NSAIDs whenever possible.
Always talk to your cardiologist or primary care provider before adding OTC pain relievers to your routine. Your heart health depends on a delicate chemical balance. Do not let a simple pain pill tip the scales.
Frequently Asked Questions
How exactly does ibuprofen cause blood pressure to rise?
Ibuprofen inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which effectively stops the production of vasodilating prostaglandins in the kidneys. Without these prostaglandins to keep blood vessels open, the kidneys experience vasoconstriction and begin to retain sodium and water, leading to increased blood volume and higher systemic vascular resistance.
How soon after taking ibuprofen will my blood pressure increase?
Clinical evidence suggests that hemodynamic changes begin within hours of ingestion as prostaglandin synthesis is blocked at the cellular level. While a single dose may not cause a hypertensive crisis, significant elevations in mean arterial pressure are often measurable within the first few days of regular use.
Is it safe to take ibuprofen if I am already on blood pressure medication like Lisinopril?
Combining ibuprofen with ACE inhibitors or ARBs is generally discouraged because it creates a “Triple Whammy” effect that can lead to acute kidney injury. The ibuprofen constricts the afferent arteriole while the blood pressure medication dilates the efferent arteriole, dangerously reducing the kidney’s internal filtration pressure.
Which over-the-counter pain reliever is safest for patients with hypertension?
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is the preferred first-line analgesic because it does not significantly inhibit renal prostaglandins or cause sodium retention. Unlike NSAIDs, it remains hemodynamically neutral and does not typically interfere with the clinical efficacy of most antihypertensive drug classes.
Does topical diclofenac gel raise blood pressure as much as oral ibuprofen?
No, topical NSAIDs like diclofenac (Voltaren Gel) have very low systemic absorption, typically around 6% compared to oral formulations. This allows for localized anti-inflammatory relief with minimal impact on renal function or systemic blood pressure, making it a much safer alternative for managing arthritis in heart patients.
Can taking ibuprofen daily lead to permanent kidney damage?
Chronic daily use of NSAIDs for more than two weeks can lead to serious complications such as papillary necrosis or chronic interstitial nephritis. In patients with pre-existing chronic kidney disease (CKD), regular ibuprofen use can accelerate the progression toward end-stage renal disease by chronically reducing renal perfusion.
Why is the risk of high blood pressure from ibuprofen higher in the elderly?
Older adults naturally have a lower glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and reduced renal physiological reserve, making their kidneys more sensitive to drug-induced vasoconstriction. Additionally, the elderly are more likely to be taking concurrent medications, such as diuretics, that compound the renal stress caused by ibuprofen.
Does ibuprofen interfere with the heart-protective benefits of low-dose aspirin?
Yes, ibuprofen can competitively inhibit the anti-platelet effect of low-dose aspirin if taken too closely together. This interaction prevents aspirin from permanently binding to COX-1 enzymes in platelets, potentially neutralizing its ability to prevent heart attacks and strokes.
Is naproxen a safer alternative to ibuprofen for blood pressure control?
While some studies suggest naproxen (Aleve) may have a slightly lower risk for certain thrombotic events, it is still an NSAID that causes renal vasoconstriction and sodium retention. It can elevate blood pressure similarly to ibuprofen and should be used with equal caution in patients with hypertension.
What are the warning signs that ibuprofen is affecting my blood pressure or kidneys?
Patients should watch for sudden weight gain of more than three pounds in a week, peripheral edema (swelling in ankles or hands), or shortness of breath. Because hypertension is often asymptomatic, I strongly recommend daily home blood pressure monitoring whenever an NSAID regimen is initiated.
How does a high-sodium diet interact with ibuprofen use?
Ibuprofen forces the kidneys to aggressively reabsorb sodium, so consuming a high-salt diet while taking the medication provides more “fuel” for fluid retention. This combination significantly compounds the increase in total blood volume and can lead to much higher blood pressure spikes than the medication alone.
Can I take ibuprofen if I have compensated heart failure?
Patients with heart failure should generally avoid ibuprofen because the resulting fluid retention increases the heart’s workload and can trigger an acute exacerbation. Even short-term use can lead to pulmonary congestion and a significantly increased risk of hospital admission for heart failure management.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The physiological effects of medication can vary significantly between individuals. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional or cardiologist before making changes to your medication regimen or starting new over-the-counter drugs.
References
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) – FDA.gov – 2015 update on strengthened warnings for non-aspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and heart risk.
- New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) – “Cardiovascular Safety of Celecoxib, Naproxen, or Ibuprofen for Arthritis” – The PRECISION Trial results regarding hemodynamic stability.
- American Heart Association (AHA) – Heart.org – Clinical guidelines on managing hypertension and the impact of OTC analgesics.
- Journal of Clinical Hypertension – “NSAIDs and Hypertension: A Review of Mechanisms and Clinical Implications” – Detailed analysis of COX inhibition and renal vasoconstriction.
- National Kidney Foundation – Kidney.org – Resources on the “Triple Whammy” effect and NSAID-induced acute kidney injury.
- Mayo Clinic – “NSAIDs: Do they increase my risk of heart attack and stroke?” – Expert insights on the cardiovascular profile of common pain relievers.