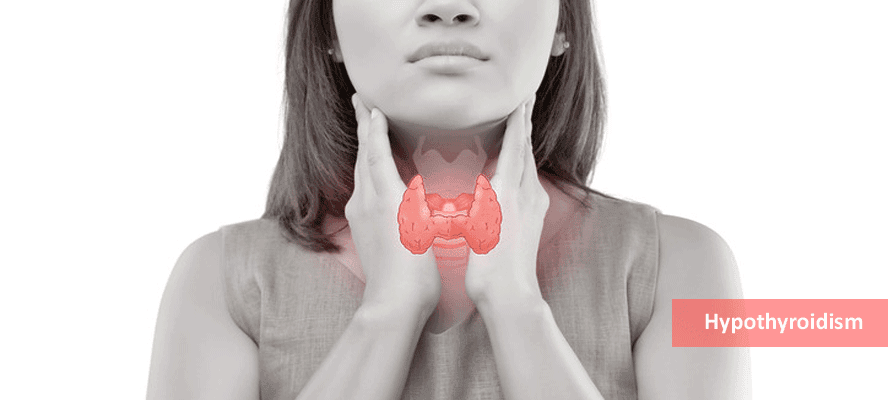
Are you feeling sudden tiredness these days without any apparent reason, experiencing dryness of skin and frequent constipation? All these could be early indications of underactive thyroid gland.
Underactive thyroid, also called hypothyroidism is a common disorder which is prevalent in India. In hypothyroidism women or older people tend to suffer more than men. Understanding this serious condition in detail would help in its effective management.