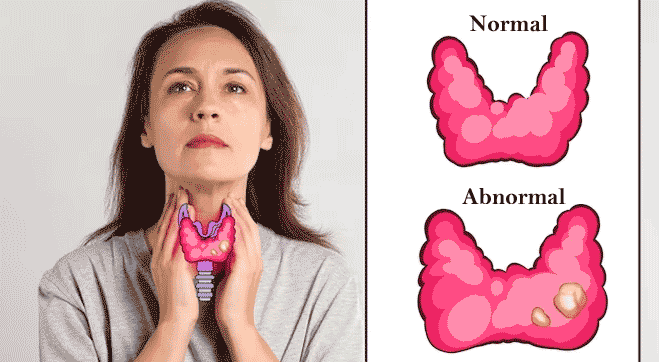
It seems magical, when a fuzzy grounded caterpillar molds into a beautiful butterfly powered with wings and flying around with alluring tinges and shades. Indistinguishable, the Butterfly shaped gland- thyroid, hidden at the base of the neck, possesses great power. thyroid gland produces hormones that control the Metabolic activities in the body. Every magical spell of hormone can sprinkle phenomenal functions that sparkle throughout the body. If the spell goes wrong, magic may go misleading or fails to occur. Sometimes, spell can turn the other way round and can attack its own self. Such a consequence of the misspelled magic of thyroid gland is said to be thyroiditis.