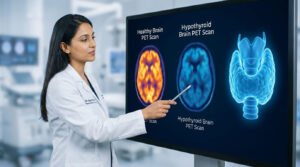
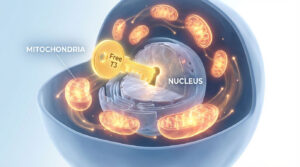
In scientific terms “infertility” means the inability of a couple to have a child (regardless of cause) after one year of unprotected sexual intercourse. When looking at the statistical data it was found that infertility problem is on the rise, where one in every six couple is suffering from it. There are many different reasons for the infertility, that it becomes difficult sometimes to pinpoint the exact cause of it. One factor that many of the people may not have on their radar is the possibility of the undiagnosed thyroid problem, which over the past few years is being recognized as an entity in a wide variety of gynecological disorders.