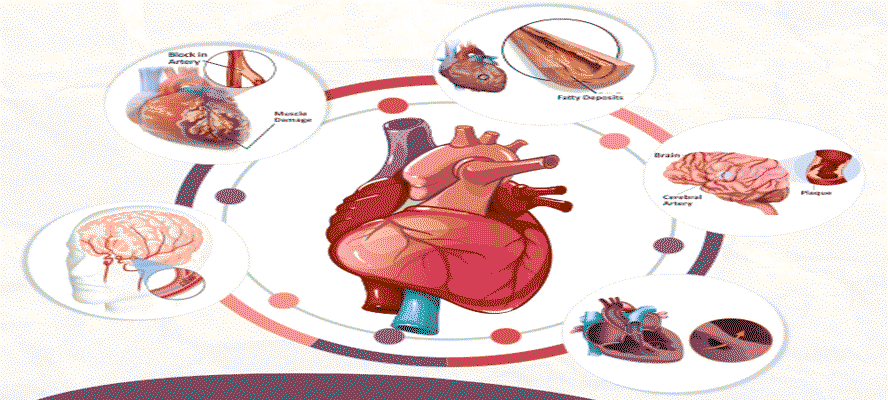
Cardiovascular Diseases Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) is an umbrella term for all conditions related to irregular functioning of the heart and blood vessels. It is one of the leading causes of death globally with an estimated 17.9 million deaths in 2019.