Urine Routine And Microscopy Test
Complete Urine Analysis (24)
- APPEARANCE
- BACTERIA
- BILE PIGMENT
- BILE SALT
- CASTS
- COLOUR
- CRYSTALS
- EPITHELIAL CELLS
- LEUCOCYTE ESTERASE
- MUCUS
- NITRITE
- PARASITE
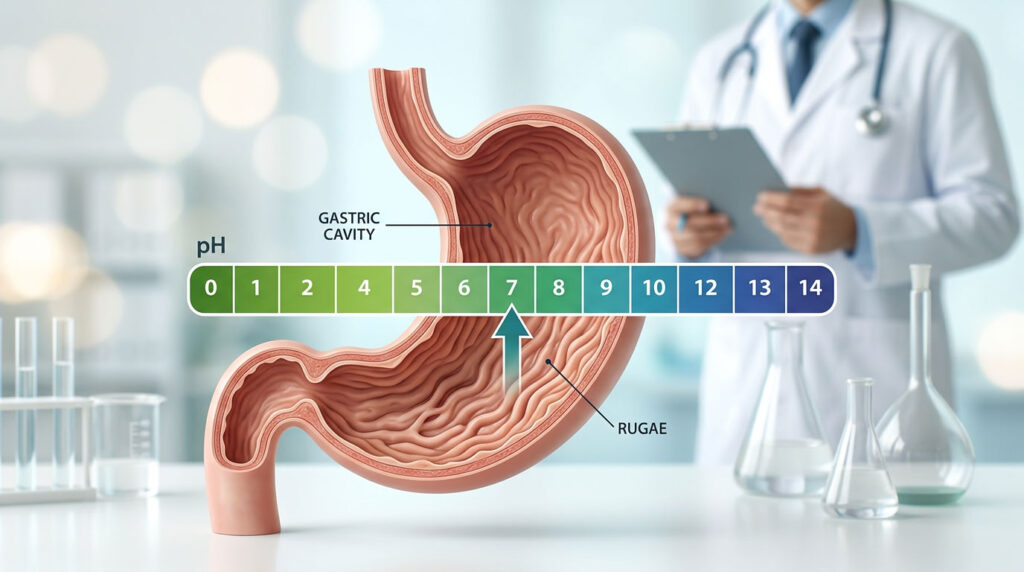
- PH
- RED BLOOD CELLS
- SPECIFIC GRAVITY
- URINARY BILIRUBIN
- URINARY GLUCOSE
- URINARY LEUCOCYTES (PUS CELLS)
- URINARY PROTEIN
- URINE BLOOD
- URINE KETONE
- UROBILINOGEN
- VOLUME
- YEAST
What Is Urine Routine Test
An urine routine test or urinalysis is usually recommended to screen for or monitor certain health conditions, such as liver diseases, kidney diseases, diabetes and urinary tract infections (UTIs). The urine analysis typically involves the visual, chemical and microscopic examination of the urine. Your healthcare provider will recommend an urine routine examination based on your symptoms or your risk factors for underlying medical conditions and complications.
About Complete Urine Analysis Test
Learn everything about urine analysis test before you book lab test online. Understand the why, how, and what of this test.
What Does Complete Urine Analysis Include?
A routine urinalysis test checks:
Visual examination – The colour and appearance of the urine is analysed during the urine examination to understand the presence or potential risk of an underlying health condition.
Chemical examination – Special test strips or dipsticks are used to gauge the presence and volume of chemical substances in the urine. The degree of colour change in the dipsticks is treated as the indicator of several health conditions.
The chemical aspect of urine analysis tests include several tests, such as:
- Protein urine tests – Used to gauge the level of albumin protein in the urine
- Urine pH level tests – Checks the acid-base balance of the urine
- Ketones urine tests – Checks the extent or potential risk of diabetic ketoacidosis
- Glucose urine tests – Measures the amount of sugar excreted in your urine
- Bilirubin urine tests – Checks for liver or bile duct complications
- Nitrite urine test – Checks for UTIs
- Leukocyte esterase urine tests – Checks for inflammation in your urinary tract or kidneys
- Urine specific gravity test – Gauges the concentration of all chemical particles in your urine
Microscopic examination – The urine routine and microscopy test is used to investigate cells, cell fragments, urinary casts, mucus, crystals, bacteria and germs.
Some of the common microscopic urine analysis tests include:
- RBC urine tests – Measures the volume of red blood cells in your urine
- WBC urine tests – Measures the volume of white blood cells in your urine
- Epithelial cells – Measures the volume of epithelial cells (cells that surround hollow body organs and urinary tracts)
- Bacteria, yeasts and parasites – Measures the presence of these microorganisms
- Urinary casts – measures the amount of urinary casts that are formed from proteins released by your kidneys
Opt for a comprehensive routine urine analysis to assess your potential risk of developing several health complications related to your heart, kidney and overall urinary system and other lifestyle disorders.
Why Do I Need An Urine Routine And Microscopy Test
Your healthcare provider will recommend an urine routine test or a urine microscopy test or both urine routine and microscopy tests:
- As a part of routine health screenings
- If you are exhibiting signs and symptoms of diabetes and kidney diseases
- To monitor the efficacy of ongoing treatments for diabetes and kidney complications
- To diagnose UTIs, pregnancy and other health conditions
An urine analysis normal report is also a prerequisite for an upcoming surgery or other invasive medical interventions.
How To Prepare For Urine Routine And Microscopy Test
If you are to opt for a urine routine test, here’s how you can prepare beforehand.
- Consume adequate levels of fluids to be able to produce an urine sample
- Consult with your healthcare provider to know the dos and don’ts about food and medications to avoid before an urinalysis as it may impact the test results
- During menstruation, certain vaginal discharges may interfere with your urine analysis test report, Seek your healthcare provider’s advice beforehand.
Urine Routine And Microscopy Test Procedure
The urine analysis test procedure is fairly simple. You will be asked to produce a clean catch urine sample, probably the first void in the morning for the visual, chemical and microscopic analysis. If you are hospitalised or are unable to move around, the urine sample will be collected through a catheter. Once you receive the routine urine examination test results, do consult with your healthcare provider for necessary preventive/treatment interventions.
Test Result Interpretation
You received your Test results but still need help determining if they fall under the normal range. Read this section to understand whether your results are within the Urinalysis normal range or not.
What Does Urinalysis Test Result Mean?
A complete urine analysis involves the visual, chemical and microscopic investigation of the urine and thus the test results on the urine analysis reports and interpretations vary.
Visual Examination
Pale to shades of yellow and even amber is considered the normal urine colour. An unusual urine colour might occur as a response to certain medications, supplements, and dietary products. Urine of other shades and a cloudy appearance may indicate
- Damage to a part of the urinary system
- Substances, such as sperm and skin cells, bacteria, RBCs, WBCs
- Medical conditions, such as dehydration, UTIs, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), kidney stones and diabetes
Chemical Examination
The results of the chemical aspect of urine analysis tests may mean different things and indicate several underlying health conditions. The results of chemical examination of the urine are categorised into positive and negative.
- Protein urine tests – High volume of proteins, such as albumins in your urine may indicate heart failure, kidney issues and extreme dehydration
- Urine pH level tests – A high urine pH level may indicate kidney complications and UTIs and a low pH level may indicate diabetes-related ketoacidosis and diarrhoea
- Ketones urine tests – High ketone concentration in your urine means that your body has to break down fats to get energy as it is not getting glucose as the source of energy, which is known as diabetic ketoacidosis
- Glucose urine tests – High glucose volume in your urine indicates diabetes or gestational diabetes
- Bilirubin urine tests – High bilirubin content may indicate that your have liver or bile duct complications
- Nitrite urine test – A positive nitrite test may confirm an UTI. However, you might still have an UTI even though your test result is negative.
- Leukocyte esterase urine tests – High leukocyte or WBC count in your urine may indicate bacterial UTIs as the core cause
- Urine specific gravity test – Abnormal results may imply several health complications
Microscopic Examination
The results of microscopic examination of urine may vary based on the type of test undertaken. The results are categorised as few, moderate and many. While few and moderate amounts of RBCs, WBCs, urinary casts and other microorganisms in your urine might not be alarming, if the counts are higher than normal, you must seek immediate diagnostic and treatment interventions.
- RBC urine tests – Higher than normal levels of red blood cells in your urine may indicate urinary bladder, kidney or urinary tract complications
- WBC urine tests – A higher leukocyte count may indicate inflammations or infections in the urinary tract
- Epithelial cells – A higher epithelial cell count might indicate infections, inflammations or cancer of the urinary tract
- Bacteria, Yeasts and Parasites – A higher presence of these microorganisms may indicate bacterial and parasitic infections of the urinary tract
- Urinary casts – Too many urinary casts might indicate an underlying kidney disease and at times, might mean nothing. It’s better to arrive at conclusive diagnosis with the help of other tests.
Why Choose HealthcareOnTime?
Convenience at Your Doorstep
Ever wished for healthcare that comes to you? HealthcareOnTime makes it a reality with doorstep lab testing, cutting out clinic hassles. No more queues or travel stress. Experience at-home sample collection, prioritizing health without time constraints. —your path to health, now just a doorstep away!
Affordable Testing with Thyrocare Partnership
Experience cost-effective lab testing at-home with HealthcareOnTime’s exclusive partnership with Thyrocare. Benefit from competitive prices while ensuring precise results. Our collaboration with Thyrocare Technologies Limited guarantees affordability without compromising on the accuracy and reliability of your lab test.
Comprehensive Health Screening
At HealthcareOnTime, we’ve got your back with our comprehensive health checkup packages! Take charge of your well-being by booking online. These packages empower you to stay ahead, catching potential issues early for timely management. It’s like having a health ally, and making informed decisions for a healthier, happier life.
Disclaimer: Although we have endeavoured to provide accurate information on this page, we strongly recommend that you seek advice from your doctor before relying on any of the test ranges or lab-test recommendations mentioned herein.
More Related Tests
Why To Book with HealthCareOnTime
17 Crores+ Samples Processed
World Class Technology Labs

25+ Years of Trust & Experience