You glance at your lab results and see that red flag next to your hemoglobin number. Immediately, your mind starts racing. Is something seriously wrong? Could this be cancer? Are you about to have a stroke?
Table of Contents
As a board-certified hematologist, I watch this exact scenario unfold in my office every week. Patients arrive full of anxiety about their thick blood, imagining the worst possible outcomes. And I get it. Seeing abnormal lab values is unnerving.
But here is what I always tell people first: an elevated blood count is a finding that needs careful investigation. It is not an automatic death sentence. In most cases, it is a highly manageable condition that we can control with real precision.
Over the years, I have walked thousands of patients through this diagnostic process. We look at everything from your genetics to your sleep habits to your daily environment. And in this guide, I am going to walk you through the same process. We will cover what high hemoglobin actually means, what causes it, the real health risks involved, and the treatment protocols that bring it under control.
Quick Answer: What Does High Hemoglobin Mean?
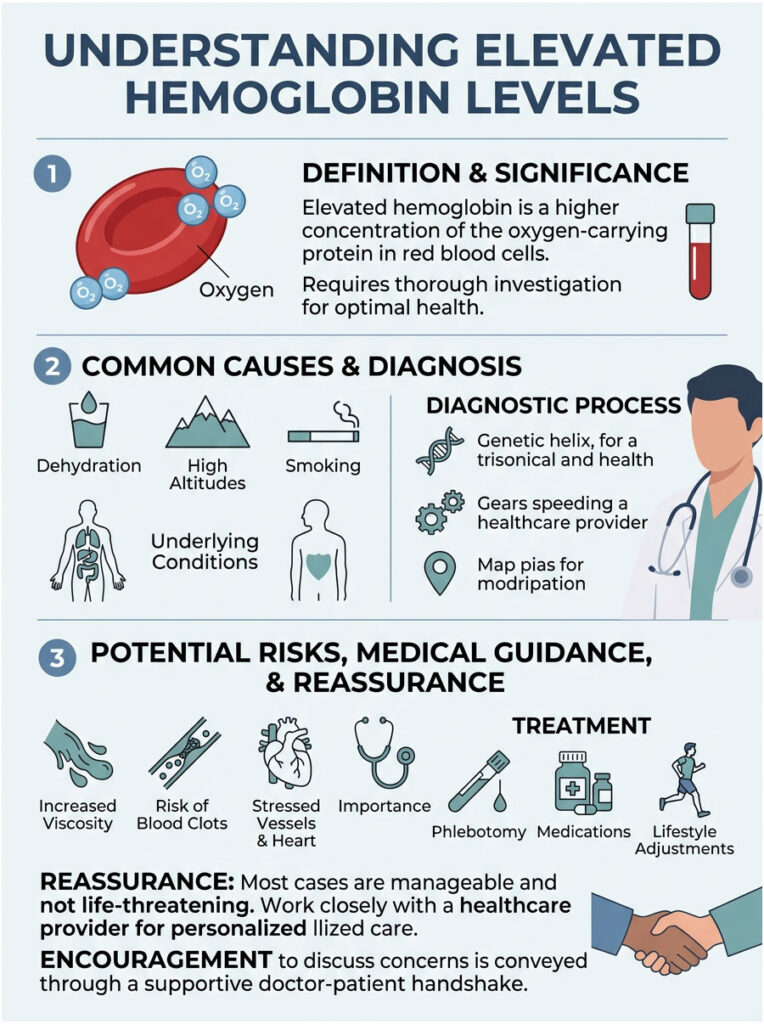
High hemoglobin, clinically known as erythrocytosis, means your blood contains an abnormally high concentration of red blood cells. This can be triggered by dehydration, chronic smoking, untreated sleep apnea, or a rare bone marrow disorder called Polycythemia Vera. When left unchecked, this cellular crowding increases blood viscosity, which raises your risk for blood clots, heart attacks, and strokes. Treatment typically involves addressing the root cause or performing therapeutic phlebotomy to safely reduce the red cell mass.
Key Statistics on Erythrocytosis
| Factor | What the Data Shows |
| JAK2 Mutation | Over 95% of Polycythemia Vera patients carry the JAK2 V617F genetic mutation. |
| Diagnostic Thresholds | Elevated levels are defined as above 16.5 g/dL for men and 16.0 g/dL for women. |
| Prevalence | Roughly 100,000 people in the U.S. are currently living with primary Polycythemia Vera. |
| Sleep Apnea Impact | Untreated severe sleep apnea can increase red blood cell mass by up to 20% over time. |
| Hematocrit Target | Keeping hematocrit below 45% significantly reduces cardiovascular death risk. |
| Smoking Effect | Carbon monoxide from cigarettes binds to red blood cells 200 times stronger than oxygen. |
Understanding the Basics: What Hemoglobin Does in Your Body
The Oxygen Delivery System
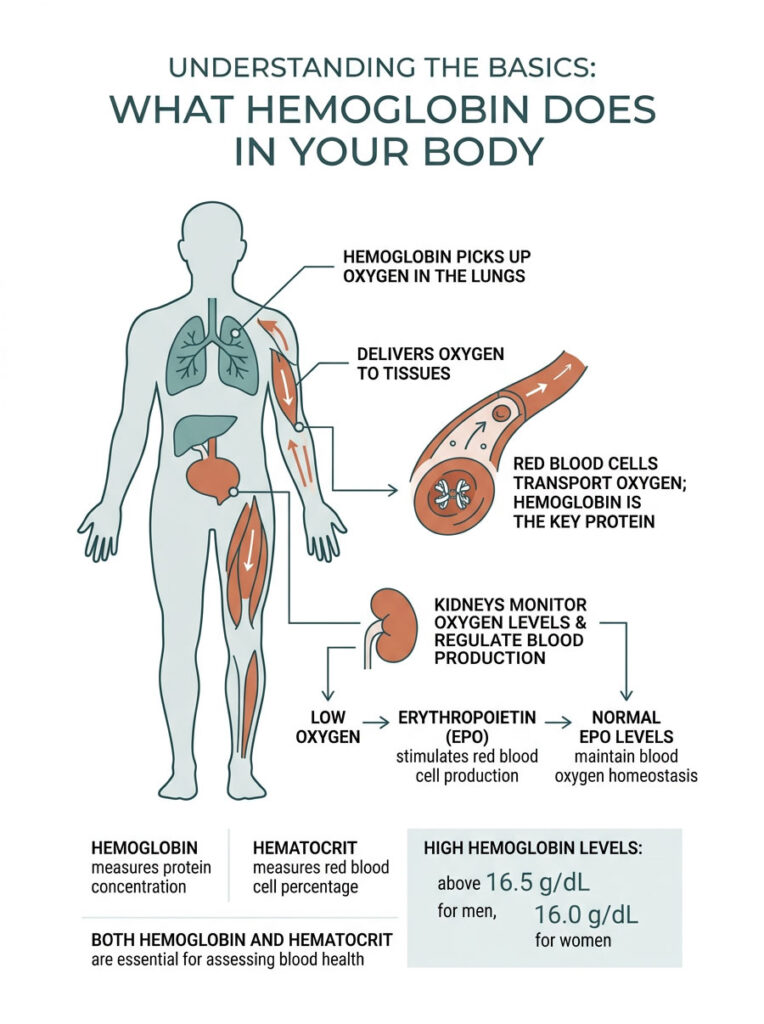
Think of your red blood cells as a massive fleet of microscopic delivery trucks. Hemoglobin is the iron-rich protein packed inside each one, and its job is to pick up fresh oxygen from your lungs and deliver it to every tissue, muscle, and organ in your body. Without this protein, your cells would suffocate within minutes.
Your body has a built-in monitoring system for this delivery network. Your kidneys act as the quality control managers. They constantly measure how much oxygen is flowing through your renal arteries, and they adjust blood production accordingly.
The EPO Feedback Loop
When your kidneys detect a drop in oxygen levels, they release a hormone called Erythropoietin, or EPO for short. This hormone travels to your bone marrow and tells it to ramp up red blood cell production. Under normal conditions, this creates a perfectly balanced loop.
When oxygen levels are adequate, the kidneys stop producing EPO, and the bone marrow slows down. The system stays in homeostasis. Problems only start when this communication network breaks down or gets tricked by something external.
When Does Hemoglobin Count as “High”?
According to the World Health Organization, the clinical thresholds are specific. For adult men, a level consistently above 16.5 grams per deciliter (g/dL) is considered elevated. For adult women, the cutoff is 16.0 g/dL. When I see numbers hovering above these markers, it triggers a formal medical investigation. These values are a signal from your body that something needs attention.
Hematocrit vs. Hemoglobin: What Is the Difference?
This is probably the most common question patients ask when they look at their lab reports. Hemoglobin measures the actual weight and concentration of the oxygen-carrying protein in your blood, expressed in grams per deciliter. Hematocrit measures the percentage of your total blood volume that is made up of red blood cells.
For example, a hematocrit of 45% means that 45% of your blood volume is red blood cells, and the rest is plasma, white blood cells, and platelets. When evaluating a patient, I always look at both numbers together to get the full picture of blood thickness.
Absolute vs. Relative High Hemoglobin: Why the Distinction Matters

Relative Erythrocytosis and Dehydration
Not every high result means your bone marrow is malfunctioning. Sometimes the problem is just an optical illusion caused by fluid loss. Doctors call this relative erythrocytosis.
Your blood has two main components: solid cells and liquid plasma. If you become severely dehydrated from illness, heat exposure, or heavy sweating, your plasma volume shrinks. With less liquid in the mix, the red blood cells appear more concentrated on a lab test. Simple dehydration is actually the single most common reason for a mild elevation on a routine summer wellness check.
Gaisboeck Syndrome and Chronic Stress
There is also a specific condition called Gaisboeck syndrome, sometimes called stress erythrocytosis. It is most often seen in middle-aged men dealing with high blood pressure and extra weight around the midsection. These patients have a chronically contracted plasma volume due to ongoing physiological stress. Their bodies are not actually making too many red blood cells. The liquid portion of their blood is just permanently low.
Can chronic stress cause elevated blood counts? Yes. Chronic physical stress, poor sleep, and untreated hypertension can all trigger this syndrome. Treating the blood pressure and reducing daily stress often brings lab values back to normal.
Absolute Erythrocytosis: The Real Overproduction
In contrast to relative cases, absolute erythrocytosis means your body is genuinely manufacturing too many red blood cells. Your total red cell mass has expanded beyond normal limits. This is where the detective work begins.
We divide absolute cases into two categories: primary and secondary. Primary means the problem originates inside the bone marrow itself. Secondary means the bone marrow is healthy but is reacting to a problem somewhere else in the body. Determining which category you fall into is the most critical step in the entire workup.
| Feature | Primary (Polycythemia Vera) | Secondary (Reactive) |
| Origin | Bone marrow stem cell defect | Response to external hypoxia |
| EPO Levels | Typically low (suppressed) | Typically high (elevated) |
| Genetic Mutation | JAK2 mutation in 95% of cases | No genetic mutation found |
| Common Triggers | Acquired genetic alteration | Hypoxia, smoking, sleep apnea, altitude |
| Treatment Approach | Phlebotomy, cytoreductive drugs | Treating the underlying cause |
Primary Causes: When the Bone Marrow Goes Rogue
Polycythemia Vera Explained
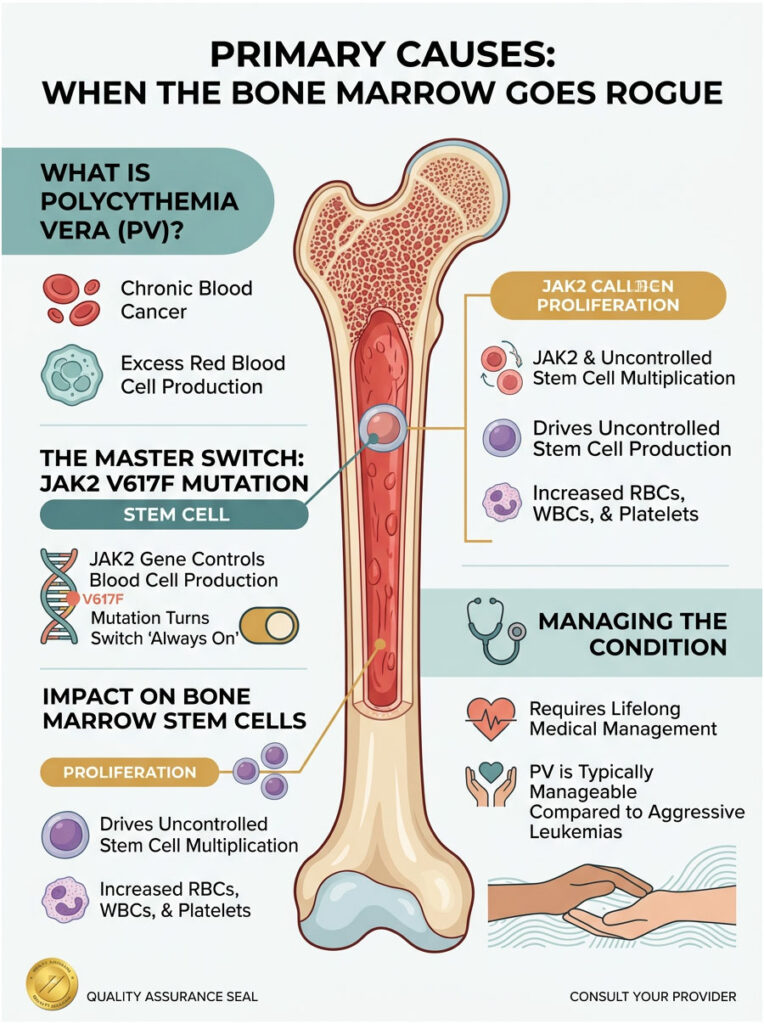
When the bone marrow starts mass-producing cells without any external signal, we evaluate for Polycythemia Vera (PV). This is a rare, chronic type of blood cancer that belongs to a family of diseases called myeloproliferative neoplasms.
I know the word “cancer” is terrifying. But I always emphasize that PV is a chronic, slow-moving condition that can be managed effectively for decades. It is not the aggressive leukemia most people imagine. In Polycythemia Vera, the bone marrow ignores the normal EPO feedback loop and manufactures massive quantities of red blood cells on its own, making the blood dangerously thick.
The JAK2 Mutation: The Broken Switch
Why does the bone marrow suddenly ignore the rules? The answer almost always comes down to a specific genetic alteration called the JAK2 V617F mutation. Think of the JAK2 gene as a master switch inside your bone marrow stem cells. Normally, it turns on when blood is needed and off when supply is sufficient.
The JAK2 mutation breaks this switch and leaves the production line permanently jammed in the “on” position. Over 95% of patients diagnosed with PV carry this exact mutation. Testing for this gene has completely transformed how we diagnose primary blood disorders.
The Stem Cell Problem
Inside the spongy center of your bones, you have pluripotent stem cells that can become any type of blood cell. When the JAK2 mutation hits one of these master cells, it creates a clone army of broken copies that eventually crowd out healthy cells.
This is why PV patients often have elevated white blood cells and platelets alongside high red counts. The entire factory is affected, causing overproduction across all three major blood cell lines. Managing this requires lifelong medical attention.
Secondary Causes: Your Body Compensating for Low Oxygen

Chronic Lung Disease and COPD
Secondary causes are far more common than primary bone marrow problems. In these cases, the body is intentionally making more blood cells to survive a low-oxygen environment. This dangerous state is called chronic hypoxia.
COPD is a textbook example. Patients with severely damaged lungs cannot absorb oxygen efficiently. Their blood oxygen saturation drops to dangerous levels, and the kidneys respond by flooding the system with EPO. The healthy bone marrow then produces extra red blood cells to compensate for the failing lungs.
Clinical note: If you have a documented history of severe asthma, emphysema, or chronic bronchitis, your elevated blood counts are almost certainly a survival mechanism. We need to fix your breathing before we can safely address the blood thickness.
Sleep Apnea and Nocturnal Oxygen Drops
Obstructive sleep apnea is one of the most common yet vastly underdiagnosed causes of secondary erythrocytosis. When your airway collapses repeatedly during sleep, your oxygen levels plummet each time you stop breathing. Your kidneys experience these episodes as repeated suffocation events.
In response, they pump out heavy doses of EPO every night. Over months and years, this nightly hormone surge produces a massive buildup of red blood cells. Many patients go through an extensive hematology workup only to discover that a CPAP machine is the real solution for their thick blood.
Smoking and Carbon Monoxide Exposure
Cigarette smoke contains high levels of carbon monoxide, an invisible gas that binds to red blood cells roughly 200 times stronger than oxygen. When carbon monoxide hijacks your red cells, it creates a toxic compound called carboxyhemoglobin. These hijacked cells become useless for oxygen transport.
Your body realizes it is suffocating at a cellular level, so the kidneys order surplus red blood cells to replace the damaged ones. This creates a dangerous cycle of increasingly thick blood. Quitting smoking is the only way to break it.
High Altitude Adaptation
Your physical environment directly affects your blood chemistry. At higher elevations, the air is thinner and contains less oxygen per breath. If you move to a high-altitude city like Denver, your body adapts by producing more red blood cells within a few weeks.
This is a normal physiological response. Hematologists always factor in a patient’s geographic location when interpreting lab results. What looks elevated at sea level may be perfectly normal at 5,000 feet.
Testosterone Therapy and Performance-Enhancing Drugs
In recent years, I have seen a massive spike in elevated counts among younger and middle-aged men. The primary culprit is almost always Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT). Exogenous testosterone directly stimulates EPO production and makes the bone marrow more sensitive to it. This creates ideal conditions for rapid red blood cell proliferation.
If you are on hormone therapy through an anti-aging clinic, your doctor must monitor your blood counts closely. We frequently have to lower testosterone doses or schedule regular blood draws to keep levels safe.
Kidney Tumors and Ectopic EPO Production
In rare cases, abnormal kidney cysts or benign tumors can trigger excessive EPO release even when the body does not need more blood. We call this ectopic hormone production. A comprehensive renal ultrasound is a mandatory part of the hematology workup for exactly this reason.
If we find a rogue cyst or tumor, surgically removing it usually resolves the high counts immediately. This is a perfect example of why we must examine the whole body, not just the blood.
Recognizing the Symptoms of High Hemoglobin and Thick Blood
The Silent Early Stage
One of the most dangerous aspects of this condition is how quiet it is at the start. In the early stages, many patients feel completely fine. They have plenty of energy, go to work, exercise, and live normally. The elevation is often discovered purely by accident during a routine annual blood panel.
This silent progression is exactly why I strongly recommend yearly blood work, especially as you get older. Establishing your personal baseline is an essential part of preventive care. You cannot treat something you do not know about.
Hyperviscosity Symptoms: When the Blood Gets Too Thick
As red cell counts continue climbing, the blood physically changes texture. It goes from smooth and fluid to sluggish and syrupy. Doctors call this hyperviscosity syndrome.
When blood is this thick, it struggles to flow through the tiny capillaries in your brain and extremities. Patients start experiencing chronic headaches that do not respond to normal painkillers, unexplained dizziness, ringing in the ears, and blurred vision. Crushing fatigue is also common because the heart has to work much harder to pump thick blood through thousands of miles of vessels.
Hallmark Signs of Polycythemia Vera
PV patients often present with specific, unusual symptoms. The most distinctive is aquagenic pruritus, an intense, burning itch that erupts immediately after a hot shower or warm bath. It is caused by abnormal histamine release from mutated blood cells called basophils. Patients describe it as thousands of tiny needles pricking the skin, and standard allergy medications do nothing to stop it.
PV patients may also develop plethora, a chronically flushed, reddish-purple complexion most visible on the face, palms, and earlobes. It looks like a permanent sunburn that never fades.
Erythromelalgia: Burning Hands and Feet
Another painful symptom linked to thick blood is erythromelalgia. This is a microvascular complication that targets the hands and feet. Tiny blood vessels become engorged and temporarily blocked by excess red cells and sticky platelets.
The result is sudden, intense burning pain in the fingers or toes. The affected area turns bright red and feels hot. A daily low-dose aspirin often provides fast, dramatic relief by preventing platelet clumping and restoring normal flow.
The Real Health Risks of High Hemoglobin
Blood Clots: The Primary Danger
This is why hematologists take elevated counts so seriously. The central danger of high hemoglobin is the dramatic increase in blood viscosity. Thick, slow-moving blood is highly prone to spontaneous clotting. When blood pools or flows too slowly, platelets clump together and form dangerous clots in the deep veins.
Patients face elevated risk for Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in the legs. If a clot breaks free, it can travel to the lungs and cause a fatal pulmonary embolism. Actively managing blood thickness is critical for preventing these events.
Arterial vs. Venous Clots
What makes primary erythrocytosis especially dangerous is that it causes clots in both veins and arteries. Most clotting disorders only affect the venous system, but thick blood spares nothing. An arterial clot in the coronary arteries causes a heart attack. A clot in the carotid arteries travels to the brain and triggers a stroke.
We also see unusual clots in the abdominal portal veins of patients with undiagnosed bone marrow disorders. A clot in the liver or spleen is a major red flag that triggers an immediate hematology workup.
High Blood Pressure and Organ Damage
Increased viscosity also drives up blood pressure. Imagine trying to suck a thick milkshake through a narrow straw. Your heart faces the same problem every second, pumping with excessive force to push viscous blood through your vessels.
Over time, this constant strain can cause the heart muscle to thicken and eventually fail. The kidneys also take significant damage under sustained high pressure, leading to chronic renal stress and eventual kidney disease.
The Bleeding Paradox
Here is one of the most confusing aspects of this condition: a disease that causes clots can also cause severe bleeding. When cell counts get extremely high, the body depletes its supply of von Willebrand factor, a crucial clotting protein. The thick blood essentially shreds this protein as it forces through tight vessels.
This leads to acquired von Willebrand syndrome. Patients may suddenly experience massive nosebleeds, bleeding gums, or gastrointestinal hemorrhages. We have to bring the counts down quickly to stop this paradoxical bleeding.
| Hemoglobin Level | Status | Associated Risks | Recommended Action |
| 13.5 to 17.5 g/dL (Men) | Normal Range | Baseline risk | Standard annual wellness check |
| 12.0 to 15.5 g/dL (Women) | Normal Range | Baseline risk | Standard annual wellness check |
| 17.5 to 18.5 g/dL | Mildly Elevated | Mild fatigue, slight viscosity increase | Hydrate, repeat CBC, evaluate lifestyle |
| Above 18.5 g/dL | Severely Elevated | High risk of clots, stroke, hyperviscosity | Urgent hematology consultation |
The Hematologist Workup: How We Diagnose High Hemoglobin

Initial Blood Panels and Oxygen Check
When you sit in my exam room, we start by verifying the numbers. We draw a fresh Complete Blood Count (CBC) with a manual differential to confirm the elevation is real and persistent. We also look closely at white blood cells and platelets. If all three lines are elevated, it strongly suggests a bone marrow problem. If only red cells are high, we lean toward a secondary cause.
Next, we check your resting oxygen saturation with a pulse oximeter clipped to your finger. If your oxygen is at 90% or lower, we immediately start investigating lung disease or heart defects.
Serum EPO: The Most Important Test
The serum Erythropoietin level is the single most important test in our initial workup. EPO acts as our clinical compass. A low EPO level means the kidneys are trying to stop blood production but the bone marrow is ignoring them. This points directly toward Polycythemia Vera.
A high EPO level means the kidneys are actively ordering extra blood. This points toward secondary causes like sleep apnea, chronic smoking, or kidney tumors. The EPO result splits our diagnostic pathway neatly in two.
Advanced Genetic Screening
If a low EPO level raises suspicion of a bone marrow disorder, we move to genetic testing. A standard blood draw is sent to a specialized molecular lab where they screen for the JAK2 V617F mutation. A positive result essentially confirms Polycythemia Vera on the spot.
If the primary JAK2 test is negative but clinical suspicion remains high, we test for the rarer JAK2 Exon 12 variant. We leave no genetic stone unturned.
Bone Marrow Biopsy
If blood tests are inconclusive, we perform a bone marrow biopsy. Many patients dread this, but it is a routine, safe outpatient procedure. We numb the skin over the back of the hip bone with local anesthetic, then use a specialized needle to extract a small liquid sample and a solid core of bone tissue.
A hematopathologist examines the sample under a microscope, evaluating cellular crowding, checking for scar tissue, and finalizing the diagnosis. This gives us the definitive answer about your blood.
Recent Advances in High Hemoglobin Treatment
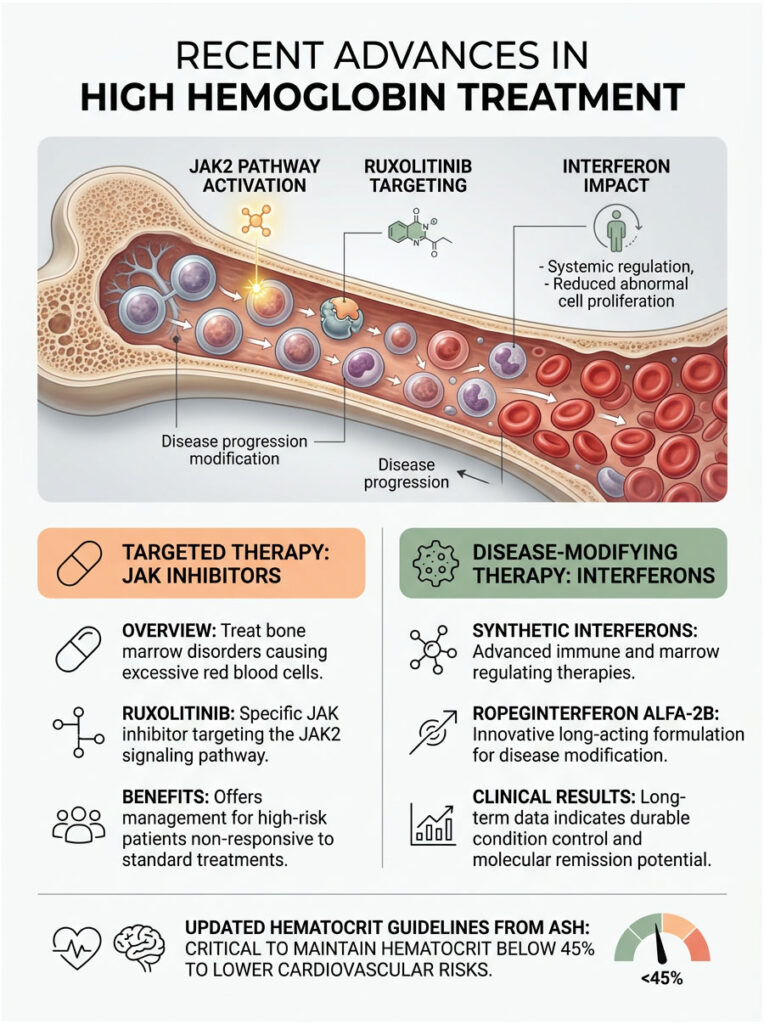
JAK Inhibitors and Targeted Therapy
Hematology is advancing rapidly. For decades, our main tool for managing bone marrow disorders was physically draining blood. Today, we have targeted therapies that work at the cellular level. JAK inhibitors like Ruxolitinib specifically block the broken JAK2 pathway, cooling down the overactive marrow, reducing spleen size, and eliminating the miserable itching. These drugs are used for high-risk patients who do not respond to standard treatments.
Interferon Therapy: Moving Toward Disease Modification
Another major breakthrough is the refined use of synthetic interferons. Ropeginterferon alfa-2b has gained significant clinical traction. Unlike older chemotherapy drugs, interferons teach your immune system to recognize and attack the mutated stem cells in the bone marrow.
Clinical trials show that long-term interferon use can actually reduce the number of mutated cells in a patient’s body. This is the closest we have to a true disease-modifying therapy for Polycythemia Vera, offering real hope for reversing the underlying genetic burden over time.
Current Hematocrit Guidelines
Recent research has refined our treatment targets. The American Society of Hematology mandates strict maintenance of hematocrit below 45% for all PV patients. Large-scale studies have proven that staying under this threshold significantly reduces cardiovascular death risk. In my clinic, 45% is the number we defend aggressively. If a patient creeps up to 46%, we schedule an intervention immediately.
Treatment Protocols and Practical Strategies

Therapeutic Phlebotomy: How It Works
If your red cell mass is dangerously high, the most effective treatment is therapeutic phlebotomy, essentially a prescription blood draw performed in a controlled medical setting. You sit in a comfortable chair while a nurse safely removes about one pint (500 mL) of blood from an arm vein. The whole process takes about twenty minutes.
This physically removes excess red cells and provides immediate relief from viscosity symptoms. Newly diagnosed patients typically need weekly phlebotomies until hematocrit drops below 45%. After that, they shift to a maintenance schedule every few months.
Aspirin and Cytoreductive Medications
Almost all affected patients are placed on daily low-dose aspirin (81 mg). This prevents platelet clumping and significantly lowers the risk of heart attacks and strokes. For high-risk patients, particularly those over 60 or with a history of blood clots, we add cytoreductive medication.
The standard drug is Hydroxyurea, a gentle chemotherapy pill taken daily. It slows down the bone marrow factory and drastically reduces the need for frequent phlebotomy visits. It is highly effective and generally well-tolerated.
Lifestyle Changes That Make a Real Difference
Medical treatments are only half the equation. Aggressive hydration is essential. Drinking plenty of water expands your plasma volume and naturally dilutes circulating red cells. I tell every patient to carry a large water bottle wherever they go.
If you smoke, you must stop. Smoking cessation is completely non-negotiable for anyone with thick blood. As soon as you stop inhaling carbon monoxide, your body will gradually stop overproducing red cells.
Diet and Iron: A Counterintuitive Approach
Here is a clinical twist that surprises many patients. Hemoglobin is built from iron. When we perform therapeutic phlebotomy, we are intentionally making you iron deficient to starve the bone marrow of its raw materials. That is why PV patients should never take iron supplements. Supplementing iron is like throwing gasoline on a fire, giving the mutated marrow exactly what it needs.
I also advise limiting highly bioavailable iron sources like large steaks and organ meats. You do not need to go vegan, but managing dietary iron helps keep blood counts stable for longer stretches between treatments.
Real Clinical Cases: What This Looks Like in Practice

Case 1: Sleep Apnea Mimicking a Blood Disorder
A 52-year-old man came to my clinic with severe morning headaches and crushing daytime fatigue. His routine labs showed hemoglobin at 18.2 g/dL. He was convinced he had leukemia. His EPO came back elevated, and his JAK2 test was negative. I noticed he was overweight with a thick neck, a classic warning sign.
An overnight sleep study revealed severe obstructive sleep apnea. He was stopping breathing 40 times per hour. We started nightly CPAP therapy. Six months later, his headaches were gone, his energy was back, and his hemoglobin had dropped to a normal 15.1 g/dL.
Case 2: Diagnosing Polycythemia Vera
A 61-year-old woman presented with intense, burning itching after every hot shower. Her doctor thought it was a skin allergy and prescribed steroid creams that did nothing. Her hemoglobin was 16.8 g/dL, which is highly abnormal for a woman, and her oxygen was a perfect 99%.
Her EPO level was completely suppressed, near zero. The JAK2 test came back positive. We diagnosed Polycythemia Vera that same week, started therapeutic phlebotomy and daily baby aspirin. Today, her hematocrit stays below 45%, the itching has vanished, and she leads a normal, active life.
Case 3: The Testosterone Therapy Problem
A 45-year-old man had been on Testosterone Replacement Therapy for two years through an anti-aging clinic. He felt great, but his hemoglobin spiked to 19.1 g/dL. His blood was dangerously thick, putting him at immediate stroke risk. He did not want to stop testosterone because of how good it made him feel.
We negotiated a compromise. We reduced his weekly testosterone dose by 30% and enrolled him in a regular phlebotomy program every eight weeks. By managing both the hormones and the blood volume, we kept him safe while maintaining his quality of life.
Key Takeaways
Seeing high hemoglobin on your lab report is stressful, but it is not a reason to panic. As we have covered in this guide, it is a medical finding that can be investigated, understood, and controlled with real precision.

Whether your elevated counts stem from summer dehydration, untreated sleep apnea, or a primary bone marrow disorder like Polycythemia Vera, modern medicine has the tools to protect you. Advanced genetic tests, targeted medications, and proven physical therapies can keep your blood flowing smoothly and your risk under control.
An elevated blood count is a warning sign that calls for professional investigation, not a reason to fear the worst. Work with a board-certified hematologist, complete a proper diagnostic workup, and follow prescribed treatments closely. You can manage high hemoglobin effectively and live well.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the clinical definition of high hemoglobin for men and women?
According to World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines, high hemoglobin, or erythrocytosis, is clinically defined as a concentration greater than 16.5 g/dL in adult men and greater than 16.0 g/dL in adult women. When levels consistently exceed these thresholds, a hematological investigation is required to determine if the cause is primary, such as a bone marrow disorder, or secondary, such as chronic hypoxia.
Can dehydration cause a false high hemoglobin reading on a blood test?
Yes, this is known as relative erythrocytosis. When you are severely dehydrated, your liquid plasma volume decreases, making the red blood cells appear more concentrated than they actually are. In these cases, the absolute red cell mass is normal, but the lack of fluid creates an optical illusion of ‘thick blood’ on a standard Complete Blood Count (CBC).
Is Polycythemia Vera considered a type of blood cancer?
Polycythemia Vera (PV) is classified as a myeloproliferative neoplasm, which is a form of chronic blood cancer. While the word ‘cancer’ is frightening, PV is typically a slow-progressing condition. It occurs when a genetic mutation, usually in the JAK2 gene, causes the bone marrow to overproduce red blood cells independently of the body’s actual needs.
What are the most common symptoms of high blood viscosity?
When blood becomes too thick (hyperviscosity), it struggles to flow through small capillaries. Patients often report ‘thick blood’ symptoms such as chronic throbbing headaches, dizziness, blurred vision, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and profound fatigue. In specific cases like Polycythemia Vera, patients may also experience aquagenic pruritus—an intense itching sensation after exposure to warm water.
How does obstructive sleep apnea lead to elevated hemoglobin levels?
Sleep apnea causes repeated episodes of nocturnal hypoxia, where oxygen levels in the blood drop significantly. The kidneys sense this oxygen deprivation and respond by releasing Erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone that signals the bone marrow to produce more red blood cells. Over time, this reactive process leads to secondary erythrocytosis as the body attempts to compensate for the lack of nighttime oxygen.
Why does Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) often cause high hemoglobin?
Exogenous testosterone has a direct stimulatory effect on erythropoiesis. It increases the production of Erythropoietin in the kidneys and suppresses hepcidin, which makes more iron available for red blood cell production. Patients on TRT must be monitored closely, as the resulting increase in hematocrit can significantly raise the risk of cardiovascular events if left unmanaged.
What is the significance of the JAK2 V617F mutation test?
The JAK2 V617F mutation test is a critical diagnostic tool used to differentiate between primary and secondary erythrocytosis. Approximately 95% of patients with Polycythemia Vera carry this specific mutation, which acts as a ‘broken switch’ that keeps red blood cell production permanently turned on. A positive result usually confirms a primary myeloproliferative disorder.
What is therapeutic phlebotomy and how does it help?
Therapeutic phlebotomy is a procedure where a specific volume of blood (usually one pint) is removed from the body to rapidly reduce blood viscosity and red cell mass. It is the gold standard treatment for managing high hemoglobin because it physically thins the blood, reducing the immediate risk of clots, strokes, and heart attacks while also inducing a controlled state of iron deficiency to slow future cell production.
Why is 45% considered the ‘magic number’ for hematocrit levels?
Clinical research has demonstrated that maintaining a hematocrit level below 45% significantly reduces the risk of cardiovascular death and thrombotic events in patients with erythrocytosis. In the hematology clinic, we use this threshold as a strict target for therapeutic interventions, including phlebotomy and cytoreductive medications like Hydroxyurea.
Can cigarette smoking lead to a high red blood cell count?
Smoking causes an elevation in hemoglobin through the inhalation of carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin 200 times more strongly than oxygen, creating carboxyhemoglobin, which is useless for oxygen transport. The body perceives this as a state of suffocation and triggers the kidneys to produce excess red blood cells to compensate for the reduced oxygen-carrying capacity.
What are the primary health risks of leaving high hemoglobin untreated?
The most dangerous risk is the formation of spontaneous blood clots, known as thrombosis. This can lead to life-threatening conditions such as Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), Pulmonary Embolism (PE), ischemic stroke, or myocardial infarction (heart attack). Additionally, chronic high viscosity puts immense mechanical strain on the heart and can lead to secondary hypertension and organ damage.
How does a hematologist use EPO levels to find the cause of thick blood?
Serum Erythropoietin (EPO) levels act as a diagnostic compass. If EPO is low, it suggests the bone marrow is acting on its own (Primary Erythrocytosis/PV). If EPO is high, it indicates the bone marrow is simply responding to an external signal, such as lung disease, smoking, or a tumor (Secondary Erythrocytosis). This distinction is the first step in determining the correct treatment protocol.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. High hemoglobin is a complex clinical finding that requires professional evaluation. Always consult a Board-Certified Hematologist or qualified healthcare professional before making health decisions or interpreting laboratory results.
References
- World Health Organization (WHO) – https://www.who.int/ – Official diagnostic thresholds and clinical guidelines for erythrocytosis and myeloid neoplasms.
- Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/ – Comprehensive data on the JAK2 V617F genetic mutation and its role in primary Polycythemia Vera.
- Cleveland Clinic – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/ – Diagnostic pathways for secondary polycythemia, including sleep apnea and renal causes.
- American Society of Hematology (ASH) – https://www.hematology.org/ – Evidence-based management guidelines for maintaining hematocrit levels below 45 percent.
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) – https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/ – Research on the physiological effects of chronic hypoxia and carboxyhemoglobin in smokers.